Building automation systems have revolutionized the way we manage the complex environments of commercial buildings. These advanced systems allow for the seamless integration and control of various building components like HVAC, lighting, and security from a single interface. With automation, facility managers like Frank can ensure their buildings are energy-efficient, comfortable, and well-maintained.
- What are building automation systems?
- Systems that allow centralized control of building operations.
- Aim for increased energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
- Integrate multiple building systems like HVAC, lighting, and security.
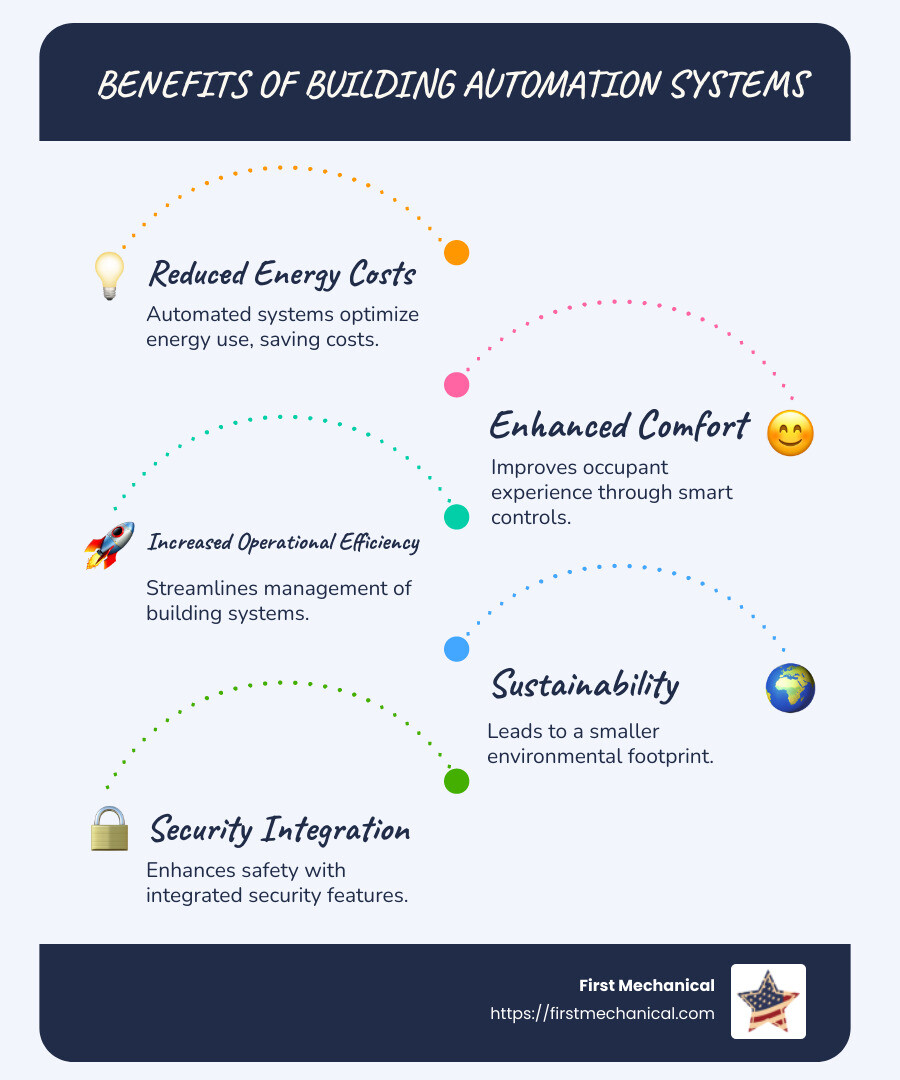
As buildings transform into smarter, more sustainable spaces, the evolution of automation technology plays a pivotal role. Smart buildings leverage automation systems not only to minimize energy wastage but also to provide improved comfort and security. An effective BAS can drastically reduce energy consumption, saving costs while increasing tenant satisfaction.
With energy being a significant operational cost, adopting automated solutions can substantially cut down on unnecessary energy usage. By utilizing data and analytics, these systems ensure that resources are used efficiently, leading to both cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint. It’s a win-win for facility managers who seek both efficiency and sustainability.
Understanding Building Automation Systems
When it comes to managing the complex operations of modern buildings, building automation systems (BAS) and building management systems (BMS) often come up. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are nuances worth understanding.
BAS vs BMS: What’s the Difference?
A BAS primarily focuses on controlling and automating the HVAC systems. It’s the backbone of building operations, ensuring heating, ventilation, and air conditioning are running efficiently. On the other hand, a BMS is broader, encompassing not just HVAC but also lighting, security, and other systems, offering a more comprehensive approach to building management.
Think of a BAS as the specialized tool for climate control within a building, while a BMS is the all-encompassing manager that oversees multiple systems to ensure they work in harmony.
Control Systems: The Heart of Automation
At the core of any building automation system are the control systems. These are the brains that process data from various sensors and make decisions about how to adjust building systems. For example, if a sensor detects that a room is too warm, the control system might decide to lower the temperature by adjusting the HVAC settings.
Control systems work tirelessly in the background, analyzing data and making real-time adjustments to optimize building performance. This not only helps in maintaining comfort but also in reducing energy waste.
Centralized Control: One Interface to Rule Them All
One of the most significant advantages of building automation systems is centralized control. Imagine having a single dashboard where you can monitor and manage all the critical systems of a building. That’s the power of centralized control in BAS.
Facility managers can quickly see the status of HVAC, lighting, and security systems, make necessary adjustments, and receive alerts if something goes wrong. This streamlined approach reduces the complexity of managing a building and increases the efficiency of operations.
Centralized control is like having a remote control for your entire building, making it easier to ensure everything runs smoothly and efficiently.
By integrating various building systems into one cohesive unit, building automation systems offer unparalleled control and efficiency. They transform buildings into smart environments that adapt to the needs of occupants while optimizing resource use.
As we dig deeper into the components of these systems, you’ll find how each part plays a crucial role in creating a seamless and efficient building management experience.
Components of Building Automation Systems
Building automation systems are like a symphony of technology working together to make buildings smart, efficient, and comfortable. Let’s break down the key components that make these systems tick.
Controllers: The Brain of the System
Controllers are the masterminds behind building automation. They take data from sensors and decide what actions to take. Think of them as the decision-makers. There are two main types of controllers:
-
Free Programmable Controllers: These allow customization. You can program them to handle unique situations specific to your building.
-
Application-Specific Controllers: These are ready-made for specific tasks, like controlling an air handler unit. You can’t reprogram them, but you can tweak settings.
Controllers are vital because they ensure everything runs smoothly, adapting to changes and optimizing building performance.
Output Devices: The Action Takers
Once controllers decide what needs to be done, output devices do the heavy lifting. These include actuators, relays, and other devices that physically adjust systems. For example, if the controller decides a room is too hot, an actuator might open a vent to let in cooler air.
Output devices are the muscles of the system, turning decisions into actions that maintain comfort and efficiency.
Communication Protocols: The Language of BAS
Just like people need a common language to communicate, building automation systems rely on communication protocols to function. Two popular protocols are BACnet MS/TP and LON FT-10. These protocols allow different parts of the system to talk to each other.
Imagine a network of Christmas lights, each bulb connected to the next. That’s how field buses connect controllers and devices, ensuring seamless communication.
User Interface: The Control Panel
The user interface is where humans interact with the building automation system. It’s the dashboard that facility managers use to monitor and control everything from HVAC to lighting. A good user interface is intuitive and provides a clear overview of the building’s status.
With a user interface, you can adjust settings, check system performance, and receive alerts if something’s amiss. It’s like having a remote control for your entire building, simplifying management and enhancing efficiency.
In summary, building automation systems bring together controllers, output devices, communication protocols, and user interfaces to create a seamless, efficient, and user-friendly building management experience. Each component plays a crucial role in changing buildings into smart environments that adapt to the needs of occupants while optimizing resource use.
Next, we’ll explore the many benefits these systems offer, from energy savings to improved comfort and sustainability.
Benefits of Building Automation Systems
Building automation systems (BAS) offer a host of benefits that make them a smart choice for modern buildings. Let’s explore how they can save energy, balance comfort and efficiency, and promote sustainability.
Energy Savings
One of the most compelling reasons to adopt building automation is the potential for energy savings. Did you know that 42% of the world’s energy is used in buildings? Yet, half of that energy can be wasted due to inefficient management. With BAS, you can dramatically cut down on this waste.
For example, when rooms are unoccupied, the system can automatically reduce HVAC output and turn off lights, slashing energy use without sacrificing comfort. This proactive approach not only reduces utility bills but also lessens the building’s carbon footprint.
Comfort vs. Efficiency
Traditionally, there was a tug-of-war between making buildings comfortable and keeping them efficient. Building automation systems resolve this by providing data-driven insights that allow you to fine-tune settings for both comfort and efficiency.
Occupants can have greater control over their environment through app-based controls, adjusting the temperature and lighting to their liking. At the same time, the system ensures that energy isn’t wasted, creating a win-win situation.
Sustainability
Sustainability is more than a buzzword; it’s a necessity. With climate change and rising energy costs, buildings must be designed to minimize their environmental impact. Building automation systems are a powerful tool in achieving this goal.
By optimizing energy use and reducing waste, BAS contribute to a building’s sustainability credentials. They help meet criteria for certifications like LEED and Green Building, which can improve a building’s value and appeal.
In summary, building automation systems are a game-changer for energy savings, comfort, and sustainability. They transform buildings into intelligent environments that adapt to the needs of occupants while optimizing resources. Next, we’ll look at the different types of building automation systems and how they cater to various needs.
Types of Building Automation Systems
Building automation systems (BAS) come in different types, each with its own unique features and benefits. Understanding these types can help you decide which system suits your building’s needs best.
Fixed Automation
Fixed automation is like a well-oiled machine. It’s designed for repetitive tasks and is best suited for environments where processes rarely change. Think of it as a factory assembly line that performs the same action over and over. Once set up, it requires minimal intervention, making it reliable but less flexible.
Programmable Automation
Programmable automation offers a bit more flexibility. Imagine a space where you can change the setup based on different needs. That’s programmable automation. It allows for adjustments in the process, but these changes require some effort and time. It’s great for buildings that have seasonal changes or different occupancy patterns throughout the year.
Flexible Automation
Flexible automation is like having a smart assistant at your fingertips. It’s designed to quickly adapt to changes with minimal effort. This type of automation is ideal for buildings that frequently change layouts or have varying needs. With flexible automation, you can easily switch between different processes, making it highly adaptable and user-friendly.
Integrated Automation
Integrated automation is the all-in-one solution. It combines multiple systems into a single, cohesive unit. Imagine a symphony where all the instruments play in harmony. This type of automation integrates HVAC, lighting, security, and more into one platform. It offers seamless control and monitoring, making it perfect for complex buildings with diverse needs.
Each type of building automation system has its strengths. Whether you need the reliability of fixed automation, the adaptability of programmable and flexible automation, or the comprehensive control of integrated automation, there’s a solution to meet your building’s demands.
Next, let’s address some frequently asked questions about building automation systems to clear up any lingering doubts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Building Automation Systems
What are the 4 types of automation systems?
When it comes to building automation systems, there are four main types:
-
Fixed Automation: This system is set up for repetitive tasks, much like an assembly line. It’s reliable but doesn’t easily adapt to changes.
-
Programmable Automation: Offers more flexibility than fixed systems. You can change settings, but it takes some effort and time. Perfect for buildings with seasonal changes.
-
Flexible Automation: Quickly adapts to changes with little effort. Ideal for spaces that frequently change layouts or have varying needs.
-
Integrated Automation: Combines multiple systems, like HVAC and lighting, into one cohesive unit. Provides seamless control and is great for complex buildings.
What are the 5 components of a building automation system?
A building automation system typically includes these five key components:
-
Controllers: These are the brains of the operation. They process data and send commands to manage building systems efficiently.
-
Output Devices: Things like actuators and relays that carry out the commands from the controllers. They make things happen, like adjusting the temperature or turning off lights.
-
Communication Protocols: The language that allows different parts of the system to talk to each other. Ensures smooth data flow and system coordination.
-
User Interface: The dashboard for users. This is where you can monitor, control, and adjust system settings easily.
-
Network Controllers: They manage data flow between the central system and field devices, ensuring everything works together harmoniously.
What is the difference between BAS and BMS?
The terms BAS (Building Automation System) and BMS (Building Management System) are often used interchangeably, but there are key differences:
-
BAS: Primarily focuses on HVAC controls. It’s about automating heating, ventilation, and air conditioning to improve efficiency and comfort.
-
BMS: A more comprehensive system. It includes HVAC but also integrates lighting, security, and other building systems for a holistic approach to building management.
Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the right system for your needs, whether it’s the HVAC focus of a BAS or the broader capabilities of a BMS.
Conclusion
At First Mechanical, we pride ourselves on providing custom HVAC solutions custom to the unique needs of our clients. Our expertise in commercial HVAC systems ensures that your building operates efficiently and comfortably, thanks to our mastery of building automation systems.
With locations across Florida, including Tampa and Melbourne, we offer comprehensive services that cover everything from installation to maintenance and emergency repairs. Our team is dedicated to optimizing your building’s performance through innovative automation technologies that reduce energy consumption and improve comfort.
By choosing First Mechanical, you’re not just getting HVAC services—you’re partnering with experts who understand the intricacies of commercial environments. We offer fast response times and reliable solutions, ensuring your building’s HVAC systems are always in top condition.
Explore our commercial HVAC building automation services to see how we can help you control your world with precision and expertise.