HVAC building automation systems are revolutionizing commercial buildings by changing them into smart, energy-efficient environments. Facility managers, like Frank, are often seeking streamlined solutions to maintain comfort, reduce energy costs, and prevent HVAC system breakdowns. These automation systems offer a way to seamlessly integrate heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems with advanced technology, ensuring optimal performance and tenant satisfaction.
-
Energy Efficiency: Automation systems help manage energy consumption intelligently, reducing unnecessary energy use.
-
Smart Buildings: With integrated systems, buildings can respond dynamically to environmental changes and occupancy patterns, enhancing livability.
-
HVAC Systems: Improve building comfort and reduce maintenance hassles with automated controls and smart sensors.
By leveraging the power of sensors, controllers, and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, HVAC building automation systems not only boost energy savings but also pave the way for healthier, more productive workspaces. Embracing these systems is not just about cutting costs—it’s about creating a sustainable future that aligns with modern building management needs.
Understanding HVAC Building Automation Systems
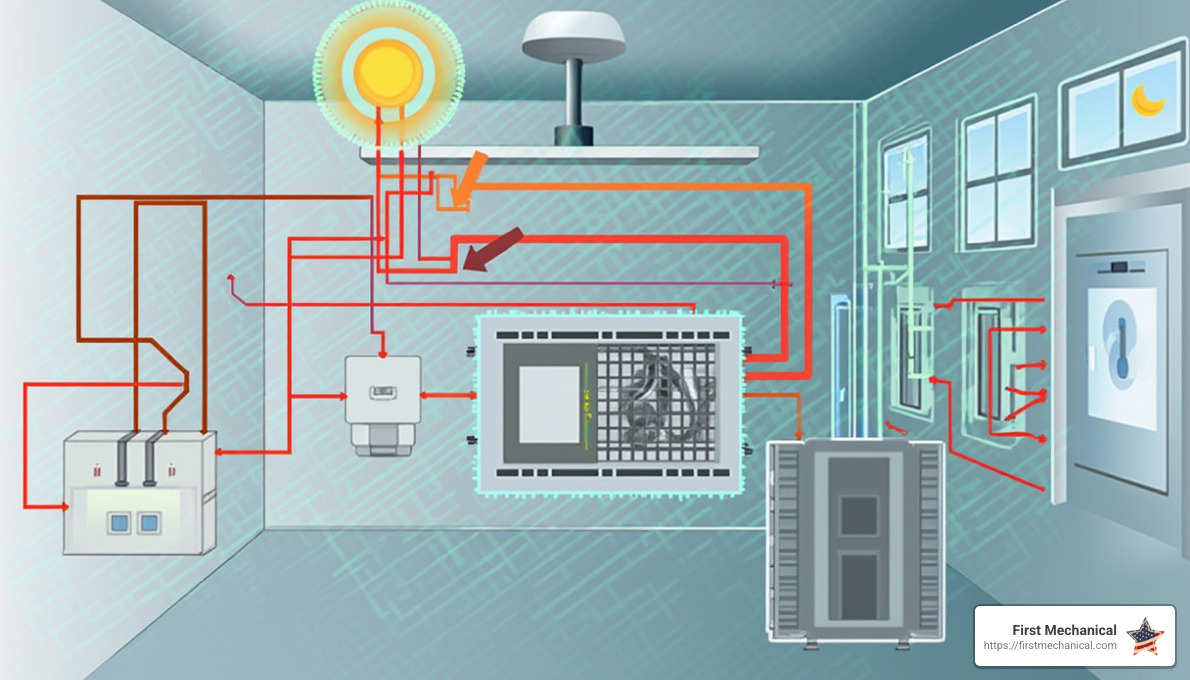
To understand HVAC building automation systems, break down their core components: sensors, controllers, and actuators. These elements work together to create a seamless and efficient indoor environment.
Sensors: The Eyes and Ears
Sensors are the backbone of any building automation system. They gather data about the building’s environment, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality. Think of them as the system’s eyes and ears. For instance, a temperature sensor detects when a room becomes too warm or cold and communicates this information to the controller.
Types of Sensors:
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor and report the current temperature.
- Humidity Sensors: Measure moisture levels in the air.
- CO2 Sensors: Detect carbon dioxide levels to ensure air quality.
- Motion Sensors: Identify occupancy to adjust lighting and HVAC settings accordingly.
Controllers: The Brain
Controllers are the brains of the operation. They receive input from sensors and make decisions based on pre-programmed logic. These decisions are then sent to actuators to adjust the building’s systems as needed.
- Field Controllers: Handle specific zones or areas within a building.
- Network Controllers: Manage the entire building’s automation network, ensuring all systems work together smoothly.
Actuators: The Muscles
Actuators are the muscle that carries out the controller’s commands. They physically adjust the HVAC components, such as opening or closing dampers, turning fans on or off, or modulating heating and cooling levels.
Examples of Actuators:
- Valve Actuators: Control the flow of water or steam in heating systems.
- Damper Actuators: Adjust air flow in ventilation systems.
- Fan Actuators: Regulate the operation of fans for optimal air circulation.
Integration for Efficiency
In smart buildings, these components work together to optimize energy use and maintain comfort. When a room is empty, sensors detect the lack of occupancy. The controller then tells the actuators to adjust the HVAC settings, like reducing heating or cooling, to save energy. This integration results in significant energy savings—up to 30% of the energy used in buildings is often wasted, and automation can help reduce that waste.
By understanding these fundamental components—sensors, controllers, and actuators—we can appreciate how HVAC building automation systems make buildings smarter and more efficient. The next section will explore the benefits these systems bring to energy savings, productivity, and overall well-being.
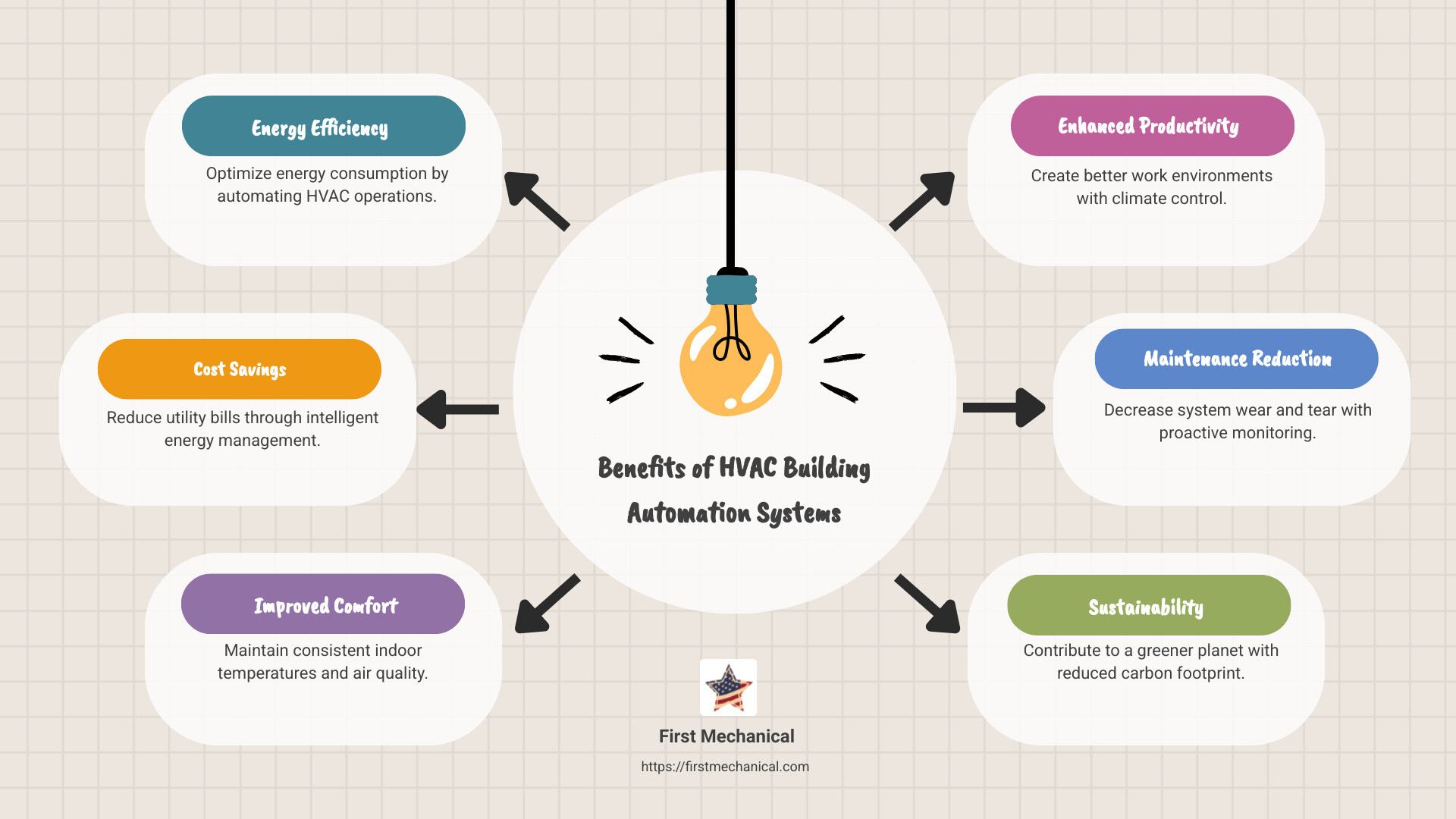
Benefits of HVAC Building Automation Systems
HVAC building automation systems offer a host of benefits that extend beyond mere temperature control. They are a game-changer in terms of energy savings, productivity, and overall well-being.
Energy Savings
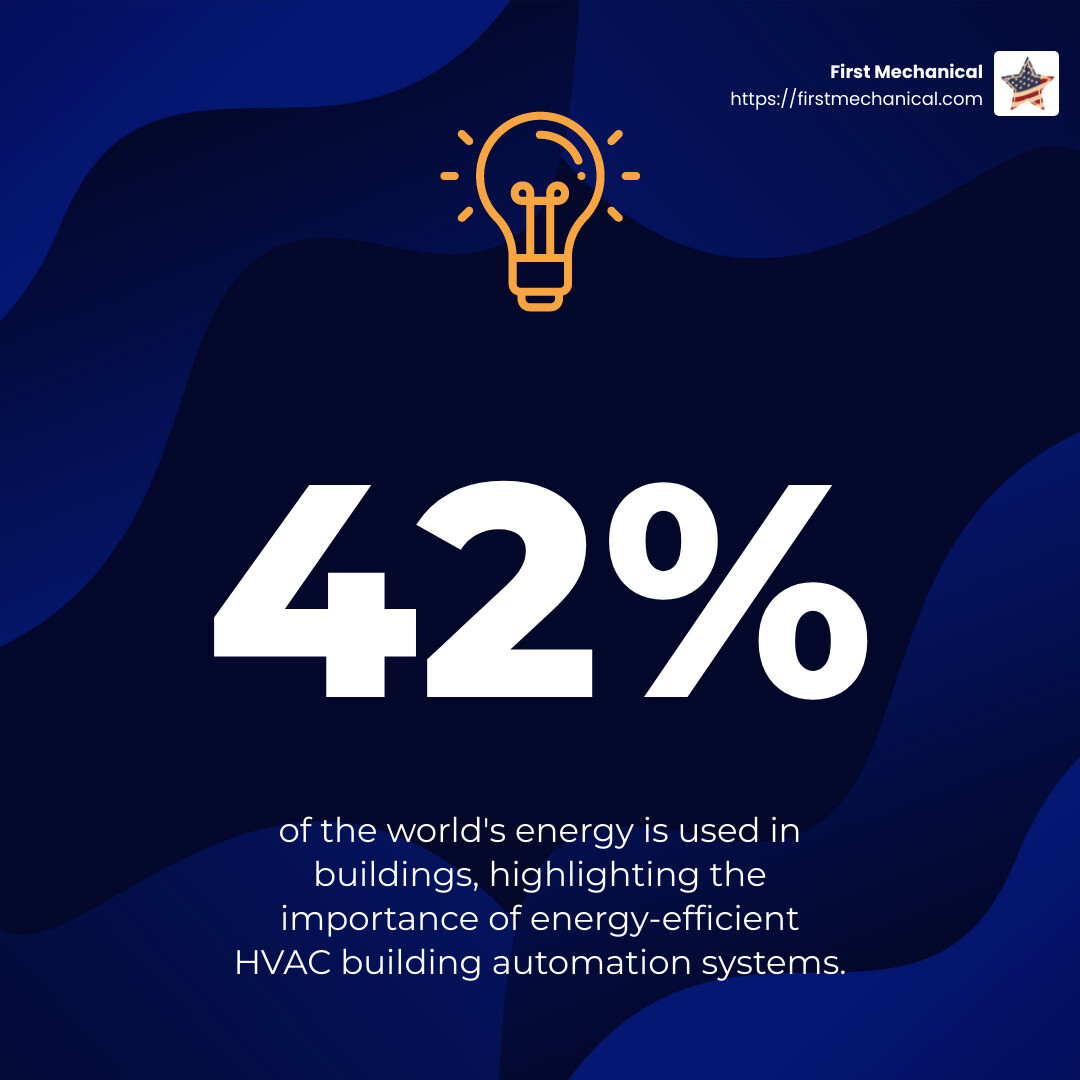
One of the most compelling advantages of HVAC automation is the potential for significant energy savings. Buildings consume a staggering 42% of the world’s energy, and much of this is wasted due to inefficient management. With automation, systems can adjust in real-time to reduce unnecessary energy use.
For instance, sensors detect when spaces are unoccupied and communicate this to the controllers, which then adjust the HVAC settings to conserve energy. This not only cuts down on waste but also slashes utility bills, making it a win-win for both the environment and your wallet.
Productivity
A comfortable environment is crucial for maintaining high levels of productivity. Automated HVAC systems ensure that temperature and air quality are consistently optimal, which helps keep occupants focused and efficient. Imagine a workspace where the climate adjusts to the number of people present, reducing the common complaints about it being too hot or too cold.
With smart HVAC controls, businesses can create personalized comfort zones custom to different needs. This flexibility means fewer distractions and more time spent on productive tasks.
Well-being
The impact of HVAC automation on well-being is often overlooked but equally important. Proper climate control contributes to healthier indoor environments by maintaining air quality and regulating humidity levels. This is particularly vital in places like hospitals, where patient comfort and safety are paramount.
A well-designed HVAC system can also help manage compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring that temperature, humidity, and air quality remain within safe and comfortable ranges. With immediate alerts and informative dashboards, facility managers can quickly address any deviations, ensuring a healthy environment for all occupants.
In summary, HVAC building automation systems are not just about energy efficiency; they’re about creating smarter, healthier, and more comfortable environments. These benefits set the stage for the next section, which will dig into the key components that make these systems work seamlessly.
Key Components of HVAC Building Automation Systems
To understand how HVAC building automation systems deliver such impressive benefits, we need to look at the key components that make them tick: sensors, controllers, and actuators.
Sensors
Sensors are the eyes and ears of an HVAC building automation system. They gather critical data on variables like temperature, humidity, CO2 levels, and occupancy. For example, when sensors detect a room is empty, they send this data to the system, prompting energy-saving adjustments.
These sensors are strategically placed throughout a building to provide real-time feedback. This constant stream of information allows the system to make precise adjustments, ensuring optimal comfort and efficiency.
Controllers
Controllers are the brain of the operation. They process the data collected by sensors and decide what actions to take. Think of them as the system’s decision-makers. They use complex algorithms to determine the best way to maintain desired conditions while minimizing energy use.
For instance, if a sensor reports that a room is getting too warm, the controller might instruct the HVAC system to increase airflow or adjust the temperature settings. These decisions are based on pre-set parameters and real-time data, ensuring a responsive and efficient system.
Actuators
Actuators are the hands of the system, carrying out the instructions given by the controllers. They physically adjust the heating, cooling, and ventilation components of the HVAC system. This includes opening or closing dampers, adjusting fan speeds, or modulating valves.
With actuators, the system can make precise changes to maintain comfort levels. They ensure that the actions decided by the controllers are executed smoothly and accurately, completing the cycle of data-driven control.
Incorporating these components effectively transforms traditional HVAC systems into smart, automated systems. This integration is the backbone of what makes modern buildings smarter and more efficient. In the next section, we’ll explore how these components work together using innovative technologies like direct digital control and programmable logic.
How HVAC Building Automation Systems Work
To truly grasp how HVAC building automation systems function, it’s crucial to understand the technologies that drive them: direct digital control, microprocessors, and programmable logic.
Direct Digital Control (DDC)
Direct Digital Control, or DDC, is the heart of modern HVAC automation. It replaces older, less efficient systems with digital precision. DDC systems use electronic networks to connect various components, allowing for seamless communication between sensors, controllers, and actuators.
This digital framework enables real-time monitoring and adjustments, which means HVAC systems can respond instantly to changes in the environment. For example, if a sensor detects a drop in room occupancy, the DDC system can quickly adjust airflow and temperature settings to save energy.
Microprocessors
Microprocessors are the tiny powerhouses that make HVAC automation possible. These small but mighty chips process the data received from sensors and execute the commands from controllers.
The introduction of microprocessors revolutionized building automation. They made controllers smaller, more powerful, and highly programmable. This advancement allowed for more complex algorithms and smarter decision-making processes in HVAC systems.
With microprocessors, building managers can easily retrofit older systems, bringing them into the digital age with minimal hassle. This adaptability is one reason why HVAC building automation systems have become so widespread.
Programmable Logic
Programmable logic is the brains behind the decision-making process. It allows HVAC systems to be customized according to specific needs and conditions. By using programmable logic, systems can follow a “sequence of operation,” a set of predefined rules for maintaining comfort and efficiency.
For instance, programmable logic can dictate that when external temperatures rise above a certain point, the system should increase cooling output while minimizing energy use. This ensures that the building remains comfortable without wasting resources.
By combining DDC, microprocessors, and programmable logic, HVAC building automation systems achieve a level of precision and efficiency that was previously unattainable. This technological synergy is what transforms ordinary buildings into smart, energy-efficient environments.
In the next section, we’ll dig into the exciting role of IoT in enhancing these systems, making them even smarter and more connected.
The Role of IoT in HVAC Building Automation
The Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping the landscape of HVAC building automation systems. By connecting devices and enabling them to communicate, IoT brings a new level of intelligence and efficiency to building management.
Smart Controllers
Smart controllers are the brain of IoT-improved HVAC systems. They use data from various sensors to make informed decisions about heating, cooling, and ventilation. For instance, if a sensor detects a sudden temperature increase in one area of a building, a smart controller can adjust the airflow to maintain comfort without manual intervention.
These controllers are not just reactive; they’re proactive. They can predict system failures before they happen, as noted by Kyle Buscher, an HVAC operations manager, who mentioned that companies like 75F often alert building managers to issues before they even notice them.
Cloud-Based Management
Cloud-based management is another game-changer in the field of building automation. By storing data in the cloud, building managers can access real-time information from anywhere. This means they can monitor and control HVAC systems remotely, optimizing performance and reducing energy consumption.
For example, Microsoft’s Global Optimization Center in Redmond uses cloud-based systems to manage data from over 45,000 sensors. This setup helped them save $1.23 million in energy costs back in 2015 by analyzing and adjusting system operations based on the data collected.
IoT Integration
Integrating IoT with HVAC systems doesn’t just improve control; it also boosts efficiency. IoT-enabled systems can use big data analytics to optimize energy usage, identify patterns, and make predictive adjustments. This is particularly valuable in commercial settings, where energy savings directly impact the bottom line.
In Tampa and other locations, businesses are already leveraging these smart technologies to create personalized comfort zones and reduce energy waste. By analyzing historical data and occupancy patterns, IoT systems can adjust settings to ensure optimal efficiency.
The combination of smart controllers, cloud-based management, and IoT integration is changing HVAC building automation systems. These advancements are not just about convenience; they represent a significant step towards smarter, more sustainable buildings.
Next, we’ll explore some frequently asked questions about these innovative systems.
Frequently Asked Questions about HVAC Building Automation Systems
What is building automation in HVAC?
Building automation in HVAC refers to the use of technology to control and monitor heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in a building. It involves sensors that detect changes in temperature, humidity, and air quality. These sensors send data to controllers, which adjust the HVAC settings to maintain comfort and efficiency. The goal is to optimize the use of utilities like electricity and water, reducing waste and energy costs.
How much does a building automation system cost per square foot?
The cost of a building automation system can vary widely, depending on factors like building size, the complexity of the system, and the specific features included. On average, costs can range from $2 to $7 per square foot. Larger buildings may benefit from economies of scale, which can lower the cost per square foot. However, the initial investment often leads to significant savings in energy costs over time, making it a wise financial decision for many property owners.
What are some examples of building automation systems?
Building automation systems encompass a variety of technologies beyond just HVAC. For instance:
- Lighting Control: Automatically adjusting lighting based on occupancy or time of day to save energy.
- Security Systems: Integrating alarms, cameras, and access controls for improved safety.
- Fire Alarms: Automated systems that detect smoke or fire and alert occupants or emergency services.
These systems work together to create a smart building environment, enhancing both safety and efficiency. In Florida locations like Tampa and Melbourne, businesses are increasingly adopting these technologies to improve building performance and occupant comfort.
Next, we’ll dig into some concluding thoughts on the impact of HVAC building automation systems.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of HVAC building automation systems, it’s clear that these technologies are a game-changer for creating smart buildings. They not only improve energy efficiency but also improve comfort and well-being for occupants.
At First Mechanical, we are committed to driving this change. Our comprehensive HVAC services, custom to meet the unique needs of each client, ensure that your commercial space is not just efficient but also future-ready. From installation to maintenance, our expertise ensures seamless integration of advanced automation technologies.
Energy conservation is at the heart of what we do. By optimizing HVAC operations, we help businesses reduce their energy consumption and lower operational costs. This is not just about saving money—it’s about contributing to a more sustainable future.
Smart building technology is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. As cities like Tampa and Melbourne continue to grow, the demand for smarter, more efficient buildings will only increase. By partnering with us, you’re not just investing in technology—you’re investing in a better, more sustainable future for your business.
To learn more about how we can help transform your building into a smart, efficient space, visit our HVAC Building Automation page. Let’s accept the future of building automation together.